Designing our Schema
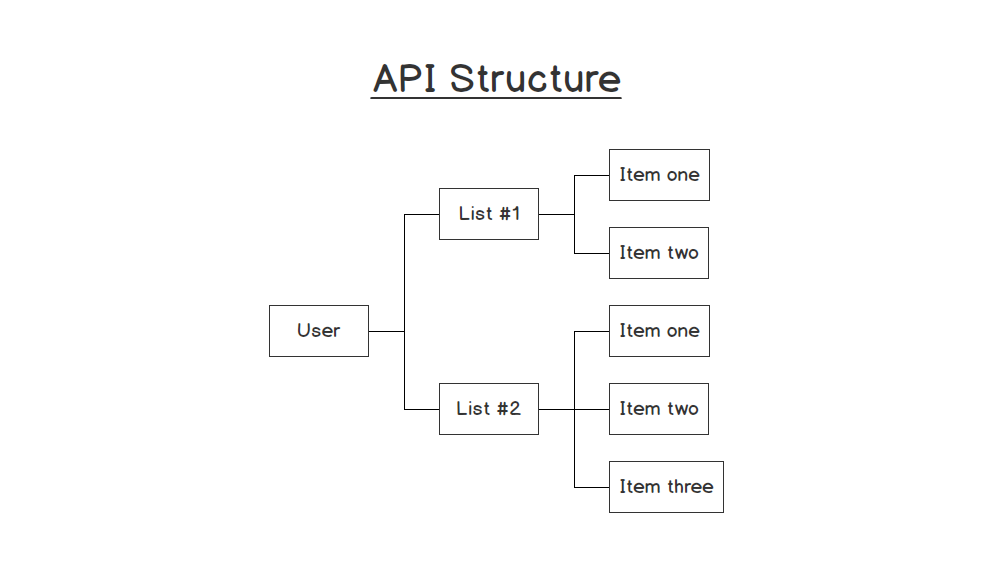
Our API Structure will look something like this (screenshot above). We will have Users, Each user can have many Lists and each List can have many Items
Open Schema section of our AWS AppSync API and you will see a page like the screenshot below. We will use this for defining our Schema i..e our Types, Queries and Mutations.
Here you can see Schema Editor and Data Types, We will add our schema in the Schema Editor.
Types:
GraphQL Types are used for defining the fields that will be accessible via GraphQL, We specify the field name and field type, Our API will make use of the following types
** The fields we specify here and the the fields we have in database can be different.
- User: For User fields
- List: For List fields
- Item: For List Item fields
User Type:
Let's create our User type, We will require user to enter full name and email address, while phone number and address can be provided optionally.
type User {
id: ID!
name: String!
email: String!
phone: String
address: String
}List Type:
For Lists, We will ask user to provide list name and description.
type List {
id: ID!
user_id: ID!
name: String!
description: String
}Item Type:
For Items, We will ask users to enter item name, description, date, status and list id.
type Item {
id: ID!
list_id: ID!
name: String!
description: String
date: String
status: Boolean!
}Queries:
GraphQL Queries are used for reading the data, like GET requests, We will make use of these queries to fetch the data from database.
The queries we define here will be available to us after deploying our API., We will make use of the following queries
- user: This will return details of the logged in user
- lists: This will return all the lists
- list: This will return only single list
- items: This will return all the items
- item: This will return only single item
Let's define our Queries.
type Query {
users: [User]
user(id: ID!): User
lists: [List]
list(id: ID!): List
items: [Item]
item(id: ID!): Item
}Mutations:
GraphQL Mutations are used for inserting and updating the data, Like POST/PATCH/PUT requests.
We will make use of these mutations for inserting and updating the data in database.
- createUser: For creating the user
- updateUser: For updating user details, resetting password
- createList: For creating a list
- updateList: For updating list details
- deleteList: For deleting list and all of items associated with it
- createItem: For creating items
- updateItem: For updating items
- deleteItem: For deleting the item
Let's define our Mutations.
type Mutation {
createUser(
name: String!,
email: String!,
password: String!,
phone: String,
address: String
): User
updateUser(
id: ID!
name: String,
email: String,
password: String,
phone: String,
address: String
): User
createList(
user_id: ID!,
name: String!,
description: String
): List
updateList(
id: ID!,
name: String,
description: String
): List
deleteList( id: ID! ): List
createItem(
list_id: ID!,
name: String!,
description: String,
date: String,
status: Boolean
) : Item
updateItem(
id: ID!,
list_id: ID,
name: String,
description: String,
date: String,
status: Boolean
) : Item
deleteItem( id: ID! ): Item
}Final Schema:
Now we need to add our Queries and Mutations to our Schema
schema {
query: Query
mutation: Mutation
}In the end our schema will finally look like this.
schema {
query: Query
mutation: Mutation
}
type User {
# id of the user
id: ID!
# name of the user
name: String!
# email of the user
email: String!
# phone number of the user
phone: String
# address of the user
address: String
}
type List {
# id of the list
id: ID!
# id of the user to whom this list belongs to
user_id: ID!
# name of the list
name: String!
# description of the list
description: String
}
type Item {
# id of the item
id: ID!
# id of the list to which this item belongs to
list_id: ID!
# name of the item
name: String!
# description of the item
description: String
# due date of this item
date: String
# whether this item has been marked as done or not.
status: Boolean!
}
type Query {
users: [User]
user(id: ID!): User
lists: [List]
list(id: ID!): List
items: [Item]
item(id: ID!): Item
}
type Mutation {
# this will add a new user in database
createUser(
name: String!,
email: String!,
password: String!,
phone: String,
address: String
): User
# this will update existing user in the database
updateUser(
id: ID!,
name: String,
email: String,
password: String,
phone: String,
address: String
): User
# this will add a new list in database
createList(user_id: ID!, name: String!, description: String): List
# this will update existing list
updateList(id: ID!, name: String, description: String): List
# this will delete a list and all of its items
deleteList(id: ID!): List
# this will add an item in the database
createItem(
list_id: ID!,
name: String!,
description: String,
date: String,
completed: Boolean
): Item
# this will update the item in database
updateItem(
id: ID!,
list_id: ID,
name: String,
description: String,
date: String,
completed: Boolean
): Item
# this will delete the item from database
deleteItem(id: ID!): Item
}Everything is same, I have just added comments.
Assuming you were writing all the above code in AWS Schema Editor, click on Save button. If you see any syntax error try to figure it our or just copy and paste this schema in the Schema Editor and it will work.
We will stop here for now.
In next Tutorial we will discuss about Creating Resources, Data Sources, Testing Queries, etc.
Until then have an awesome time.
Update Next Tutorial: Attaching Resolver to Our Mutations and Queries
Meta Information
December 18, 2017 at 11:35 AM, updated on December 19, 2017 at 12:30 AM and is written by Dhruv Kumar Jha (me).